Earth Science is a fascinating and interdisciplinary field that seeks to understand the Earth’s systems, history, and processes. As humanity faces increasing environmental challenges, Earth Science provides essential insights into natural phenomena, climate change, resource management, and disaster mitigation. This comprehensive guide dives deep into Earth Science, unraveling its branches, significance, and role in shaping our understanding of the planet.
Table of Contents
ToggleWhat is Earth Science?
Earth Science, also known as geoscience, is the study of Earth and its components, including its atmosphere, hydrosphere, lithosphere, and biosphere. It bridges physics, chemistry, biology, and mathematics to explore our planet’s dynamic systems. This scientific discipline helps us understand Earth’s past, predict future changes, and develop strategies for sustainable living.
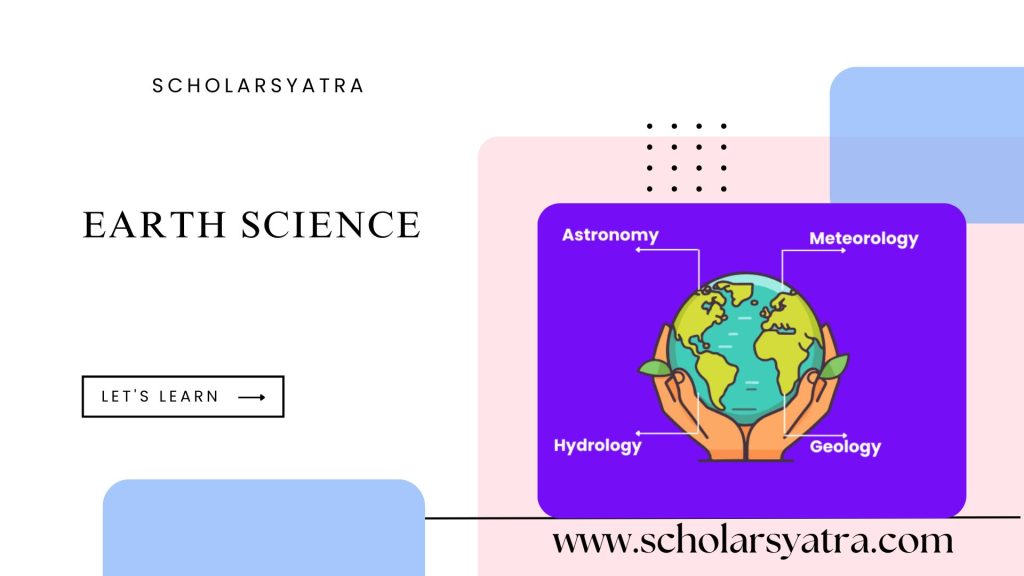
Branches of Earth Science
Earth Science is divided into four main branches, each focusing on different aspects of the planet:
1. Geology
Geology studies Earth’s solid materials—rocks, minerals, and the processes that shape the planet’s crust. Geologists investigate topics like plate tectonics, mountain formation, and the origins of earthquakes and volcanoes. They also explore the history recorded in rock layers to uncover Earth’s evolution over billions of years.
2. Meteorology
Meteorology focuses on the atmosphere and weather phenomena. Meteorologists study climate patterns, atmospheric dynamics, and weather forecasting to help predict storms, droughts, and other climatic events. Understanding meteorology is essential for preparing for extreme weather conditions and mitigating their impacts.
3. Oceanography
Oceanography examines the Earth’s oceans, covering their physical, chemical, biological, and geological aspects. Oceanographers study ocean currents, marine ecosystems, and seabed geology. This branch is vital for understanding global climate regulation and the health of marine environments.
4. Astronomy
While often associated with the study of celestial bodies, astronomy overlaps with Earth Science by exploring Earth’s place in the universe. For example, research into meteor impacts and the influence of solar radiation falls under this category.
Importance of Earth Science
1. Climate Change and Environmental Management
Earth Science provides the foundation for understanding climate change and its consequences. Scientists can predict future climate scenarios and devise strategies to mitigate global warming by studying ice cores, atmospheric patterns, and ocean temperatures.
2. Natural Disaster Preparedness
Earth scientists play a critical role in disaster risk reduction. By studying seismic activity, volcanic eruptions, and weather patterns, they develop early warning systems to protect lives and property.
3. Resource Management
Earth Science helps locate and manage natural resources like water, minerals, and fossil fuels. Sustainable resource use depends on understanding Earth’s geological and environmental processes.
4. Space Exploration
The study of Earth’s geology and atmosphere informs our exploration of other planets. Comparative planetology, which compares Earth with celestial bodies, relies heavily on Earth Science principles.
Tools and Techniques in Earth Science
- Remote Sensing and Satellite Imaging: Used to monitor landforms, weather systems, and environmental changes.
- Seismology: Studies vibrations within the Earth to understand earthquakes and the planet’s internal structure.
- Radiometric Dating: Determines the age of rocks and fossils, revealing Earth’s history.
- GIS (Geographic Information Systems): Maps and analyzes spatial data for research and planning.
- Field Surveys: Collects ground-level data on geological formations, ecosystems, and more.
Earth Science and Modern Challenges
Sustainable Development
Earth Science contributes to achieving the United Nations Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) by promoting responsible resource management, reducing disaster risks, and addressing climate change.
Urban Planning
Geoscience informs urban development by identifying stable land, managing water resources, and mitigating hazards like landslides and floods.
Biodiversity Conservation
Understanding Earth’s ecosystems enables scientists to protect biodiversity and maintain ecological balance.
Careers in Earth Science
With a degree in Earth Science, career opportunities span across industries like environmental consulting, energy, education, government agencies, and space exploration. Common roles include:
- Geologist
- Meteorologist
- Oceanographer
- Environmental Scientist
- Climate Analyst
How to Get Started with Earth Science?
1. Pursue Formal Education
Enroll in Earth Science or related courses at a university level. Many programs offer specializations in geology, meteorology, or environmental science.
2. Gain Practical Experience
Participate in fieldwork, internships, or citizen science projects to develop hands-on skills.
3. Stay Informed
Follow scientific journals, attend conferences, and stay updated on the latest research and technologies.
Earth science is the study of the Earth’s structure, properties, processes, and four and a half billion years of biotic evolution. Understanding these phenomena is essential to the maintenance of life on the planet. Sustaining our existence requires a scientific understanding of the natural materials and processes linking the geosphere, hydrosphere, atmosphere, and biosphere. Life prospers or fails at the surface of the Earth where these environments intersect.
Happy Learning! Go Green!!